Enterprise Resource Planning ERP Definition, Pros, & Cons

This includes providing comprehensive training on the new system for all affected employees and ongoing support and resources to help them adapt to the new system. By investing in employee training and support, organizations can ensure that their employees are well-equipped to use the new system effectively and maximize its benefits. This includes developing a detailed project plan, setting realistic timelines, and allocating appropriate resources to the project.

What is our editorial process?
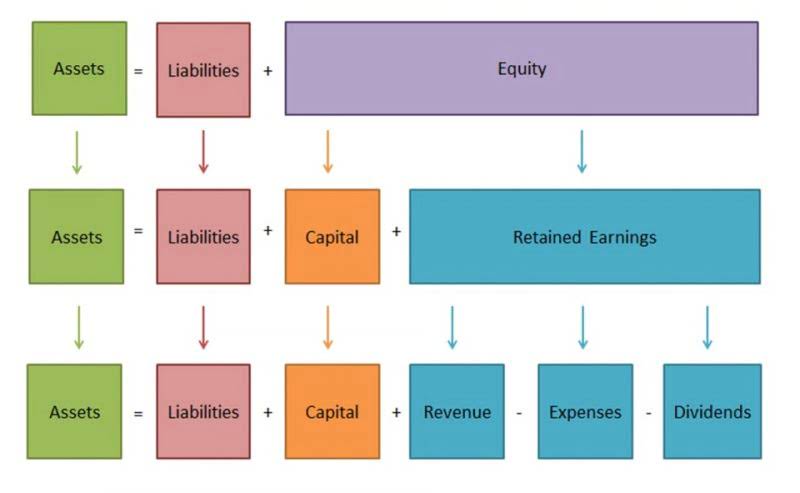
Accurate and complete reporting help companies adequately plan, budget, forecast, and communicate the state of operations to the organization and interested parties, such as shareholders. ERP has evolved over the years from traditional software models that made use of physical client servers and manual entry systems to cloud-based software with remote, web-based access. The platform is generally maintained by the company that created it, with client companies renting services provided by the platform.

Benefits
The DevX Technology Glossary is reviewed by technology experts and writers from our community. Our reviewers have a strong technical background in software development, engineering, and startup businesses. They are experts with real-world experience working in the tech industry and academia. As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, they will further enhance the law firm chart of accounts capabilities of ERP systems, helping businesses become even more agile, efficient, and responsive to changing market conditions. In today’s fast-paced business environment, understanding “what is ERP” and leveraging it is crucial for organizations looking to stay ahead of the competition. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of ERP, its evolution, key components, benefits, and future trends, helping you confidently navigate the ERP world.
Related Finance Terms
A company could experience cost overruns if its ERP system is not implemented carefully. The next generation of young workers have grown up with seamless technology that is mobile, easy to use, and always-on. No company that continues to rely purely with on-premises technology will be able to recruit top talent, regardless of age. Since data is the lifeblood of every modern company, ERP makes it easier to collect, organize, analyze, and distribute this information to every individual and system that needs it to best fulfill their role and responsibility. Open-source ERP systems have code available to the public, thus allowing for customization.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
They can automate processes that used to require heavy manual intervention, such as reconciling financial accounts. In addition, users gain a comprehensive, real-time understanding of enterprise business activities not only in the front office, but also in warehouses, on factory floors, and everywhere else across the enterprise. This knowledge is then readily available to every appropriate employee on their mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets. A business intelligence module accumulates and inspects data from various sources and helps users define a better organization’s solution. Some notable features include scheduled reporting, visualization tools, customizable dashboards, and real-time data access. When selecting an ERP system, businesses should consider their specific needs and requirements, such as the size of the organization, the number of employees, the business processes that need to be integrated, and the available budget.
An ERP system collects, stores, and manages data related to these business activities, providing a single-source overview that contributes to more efficient decision-making and overall operational effectiveness. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems serve a critical role in optimizing and synchronizing various operations within a business. The central purpose of this technology is to streamline the flow of information across different departments including finance, supply chain, human resources, customer relations, and more. ERPs effectively fetch data from different branches of a company and unify it in a centralized database. For instance, in manufacturing companies, ERP systems can track product production in real time, manage inventories, and even automate ordering of raw materials when necessary.
Human Resources and Talent Management
Then, they check availability of the product in the inventory management module (or a part of order management with access to inventory data) and return to order management to arrange shipping. The accounting and finance module keeps track of the organization’s finances, including allocations, planning, accounting, revenue control, and tax management. Next, consider any industry-specific requirements that may apply to your organization. Some industries have unique regulatory or compliance requirements, while others may have specific functional needs that are not addressed by generic ERP solutions. By selecting an ERP system that has been designed with your industry in mind, you can ensure that your organization’s unique needs are met.
- In ERP systems users have specific roles and permissions according to which they are granted access to relevant modules.
- There’s a number of different ERP solutions that can meet a variety of business needs.
- ERP systems are based on various different modules that are there to support specific business processes.
- How can these solutions manage organizations day-to-day business activities, such as accounting, finance, procurement, project management, supply chain, and manufacturing.
- In addition to these core functions, supply chain and logistics modules can also support other related activities, such as supplier collaboration, trade compliance, and reverse logistics.
- To effectively measure ERP performance and ROI, organizations should begin by setting clear goals and objectives for the implementation, such as improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing collaboration between departments.
- ERP systems can help organizations maintain better financial control by providing accurate and timely financial data, enabling them to comply with regulations and standards.
When the manufacturing industry started booming in the 1980s, new software emerged to integrate all of these processes in one place. In the 1990s, ERP was introduced, combining accounting, finance, sales, manufacturing, inventory, human resources, and project management. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) refers to software, tools, and technology you can use to manage daily business operations and automate processes, such bookkeeping as accounting, supply chain, manufacturing, managing projects, and more.
- Reporting to the program’s executive team should be a business project manager and an IT project manager.
- The biggest savings usually come with multi-tenant SaaS ERP, a type of cloud ERP where different customers share the same copy of the software, which provides economies of scale that allow the vendor to pass some savings along.
- The CIO works closely with the executive sponsor to ensure adequate attention is paid to integration with existing systems, data migration, and infrastructure upgrades.
- Notable features include inventory, purchasing, shipping, tracking, refunds, claim processing, and supplier scheduling.
- An ERP system typically includes modules that cover different business functions such as finance, human resources, sales and marketing, inventory management, and supply chain management.
- See the industry-leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) cloud solution, serving as your integrated management of business processes and applications, to gain resilience and real-time agility, to position yourself for growth.
- When ERP software is delivered as a service in the cloud, it runs on a network of remote servers instead of inside a company’s server room.
- Some of the most common functional areas an ERP system addresses include finance, procurement, manufacturing, supply chain, and human resources.
- Direct integration – ERP systems have connectivity (communications to plant floor equipment) as part of their product offering.
- Cloud computing’s internet connectivity made it easier for companies to connect their ERP systems to customers, suppliers and partners.
- You can select an ERP system that best supports your organization’s goals and objectives by carefully considering these factors.
- Next-generation technologies, like artificial intelligence (AI), help cloud-based systems rapidly improve their capabilities with no need for periodic updates, unlike your legacy system.
- While on-premise ERP solutions offer greater control and customization, cloud-based solutions can provide flexibility, scalability, and cost savings.
While stand-alone accounting software and ERP software do present similarly, the two systems are different. Accounting software typically covers financial reporting, accounts payable and receivable, banking and basic sales revenue information. The business applications, known as enterprise modules, each focus on a specific business area but work together to meet the company’s needs. Since businesses range in size and needs and no two are alike, modules are not a one-size-fits-all approach. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is enterprise resources definition software developed to manage and optimize business operations and processes.
